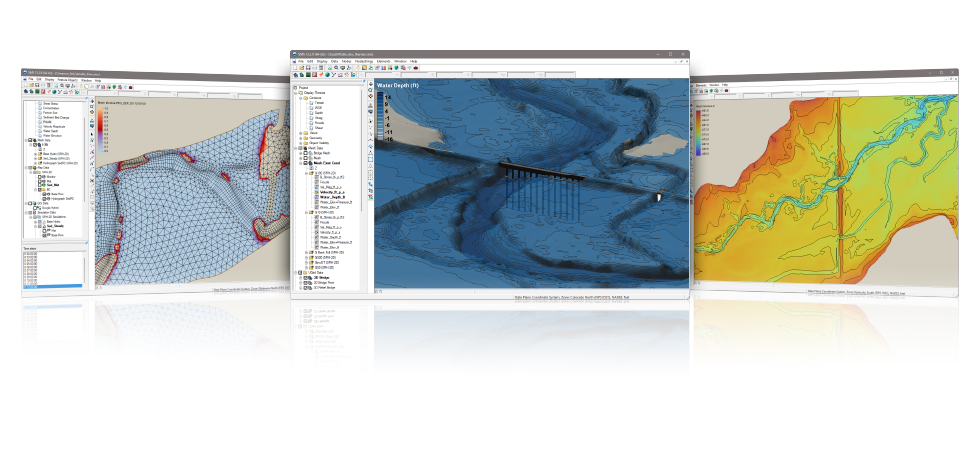
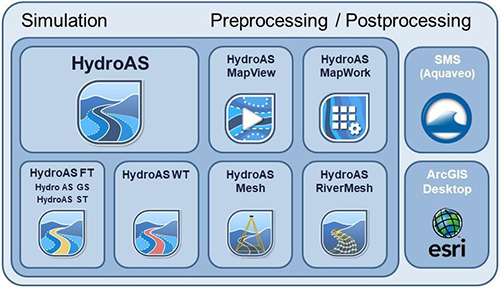
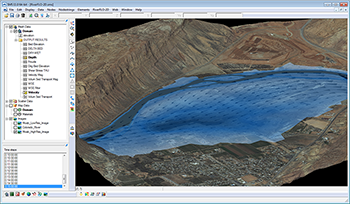
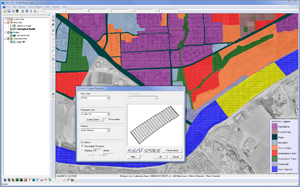
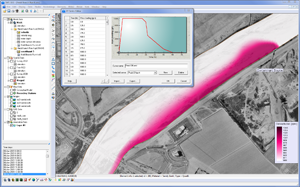
| Models |
Category |
Type |
Method |
|
Description |
| ADCIRC |
Coastal Modeling |
2D |
Finite Element |
 |
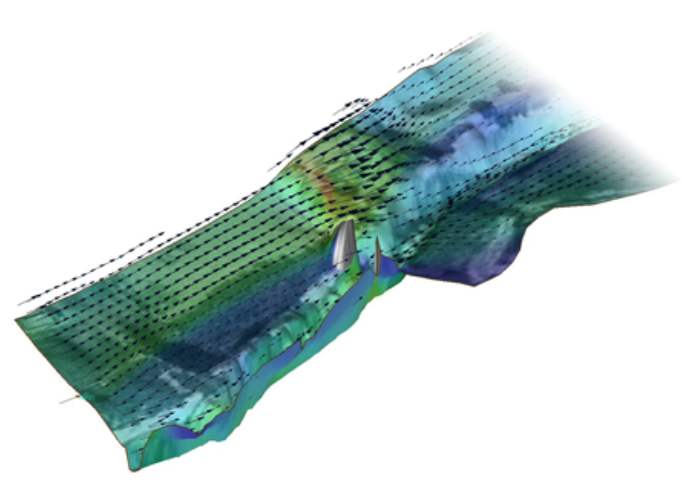
ADCIRC is a 2D, depth-integrated, baratropic time-dependent long-wave, hydrodynamic circulation model used for modeling tides and wind driven circulation, analysis of hurricane storm surge and flooding, dredging feasibility and material disposal studies, larval transport studies, and near shore marine operations. |
| CGWAVE |
Coastal Modeling |
2D |
Finite Element |
 |
CGWAVE is a 2D wave transformation model that can be used to predict wave properties such as wave heights, velocities, pressures, and radiation stresses. The model can be used to simultaneously simulate the effects of refraction, diffraction, reflections by bathymetry and structures, dissipation due to friction and breaking, and nonlinear amplitude dispersion. |
| CMS Flow |
Coastal Modeling |
2D |
Finite Element |
 |
CMS Flow includes the capabilities to compute both hydrodynamics (water levels and current flow values under any combination of tide, wind, surge, waves and river flow) sediment transport as bedload, suspended load, and total load, and morphology change. |
| CMS Wave |
Coastal Modeling |
2D |
Finite difference |
 |
CMS Wave is a 2D wave spectral transformation model that employs a forward-marching, finite-difference method to solve the wave action conservation equation. |
| BOUSS-2D |
Coastal Modeling |
2D |
Finite difference |
 |
BOUSS-2D is a numerical model for simulating the propagation and transformation of waves in coastal regions and harbors based on a time-domain solution of Boussinesq-type equations. |
| STWAVE |
Coastal Modeling |
2D |
Finite difference |
 |
STWAVE is a steady-state spectral model based on the wave action balance equation. STWAVE simulates depth-induced wave refraction and shoaling, current-induced refraction and shoaling, depth- and steepness-induced wave breaking, diffraction, and wave growth. |
| GENCADE |
Coastal Modeling |
1D |
N/A |
 |
GENCADE simulates shoreline change relative to regional morphologic constraints upon which these processes take place. The model supports responses to imposed wave conditions, coastal structures, and other engineering activity (e.g., beach nourishment). |
| WAM |
Coastal Modeling |
2D |
N/A |
 |
WAM is a global ocean wave prediction model that predicts directional spectra as well as wave properties such as significant height, mean wave direction and frequency, mean wave direction and frequency, swell wave height and mean direction etc. |
| TUFLOW |
Riverine and Coastal Modeling |
1D/2D |
Finite difference |
 |
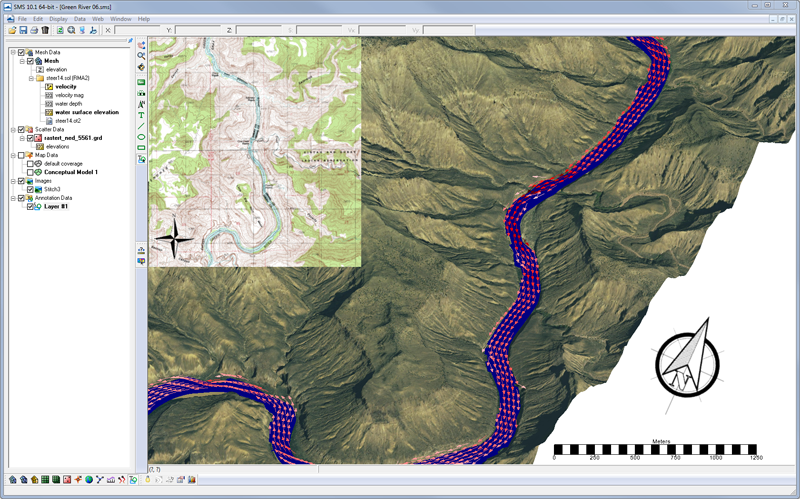
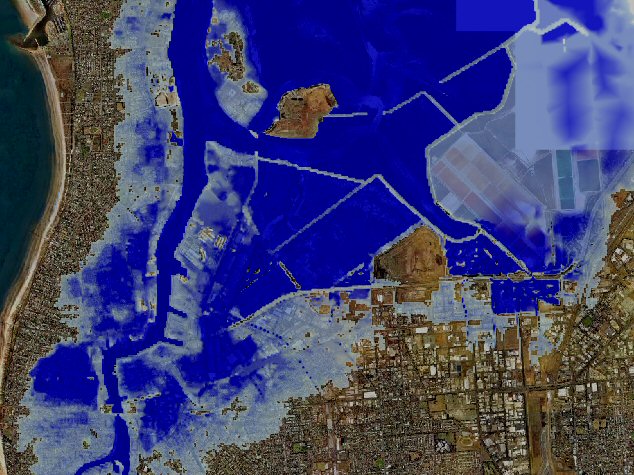
TUFLOW is a 1D and 2D numerical model used to simulate flow and tidal wave propagation. TUFLOW is designed to simulate flooding of rivers and creeks with complex flow patterns, overland and piped flows through urban areas as well as estuarine and coastal tide hydraulics and inundation from storm tides and tsunamis. |
| TUFLOW AD |
|
|
|
 |
TUFLOW AD (Advection Dispersion) is a TUFLOW module for simulating depth-averaged, two and one-dimensional constituent fate and transport for both dissolved and particulate constituents. |
| TUFLOW GPU |
|
|
|
 |
TUFLOW GPU is a TUFLOW module that uses the computational performance of GPUs to deliver a 10 to 100 times speed increase. |
| TUFLOW Multiple Domains |
|
|
|
 |
TUFLOW Multiple Domains is a TUFLOW module that allows any number of 2D domains of different cell size and orientation to be built into a model. The 2D domains can be linked by 1D domains, or via the 2D/2D linking feature. Each domain can be of different cell size, orientation and extent. |
| TUFLOW FV |
Riverine and Coastal Modeling |
2D |
Finite Volume |
 |
TUFLOW FV is used to simulate hydrodynamic, sediment transport and water quality processes in oceans, coastal waters, estuaries, and rivers. |
| PTM |
Riverine and Coastal Modeling |
N/A |
N/A |
 |
The Partical Tracking Model (PTM) is a Lagrangian particle tracker designed to allow the user to simulate particle transport processes and is used in coastal projects including dredged material dispersion and fate, sediment pathway and fate, and consitituent tranport. |
| Generic Model Interface |
Riverine and Coastal Modeling |
N/A |
N/A |
 |
SMS has a generic interface whereby any two-dimensional finite element or finite difference model can be run using SMS as a pre- and post-processor. |
| Dynamic Model Interface |
Riverine and Coastal Modeling |
N/A |
N/A |
 |
The dynamic model interface is a more flexible and powerful alternative to the generic model interface that has been supported by SMS for several years. This methodology allows a model developer to define all the attributes of an interface for a specific model in an XML file. SMS will read this file when launched, and then interact with the model. |