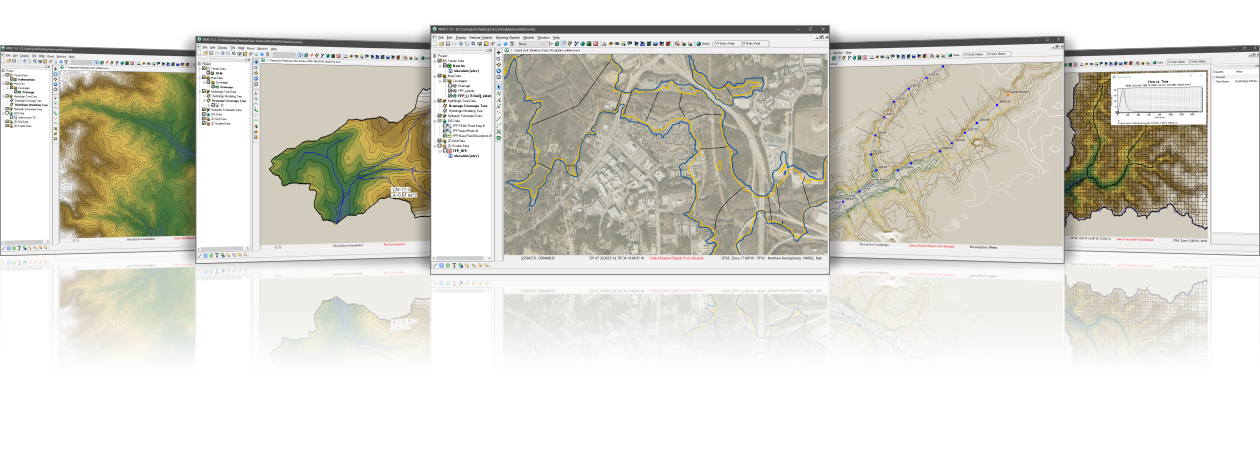
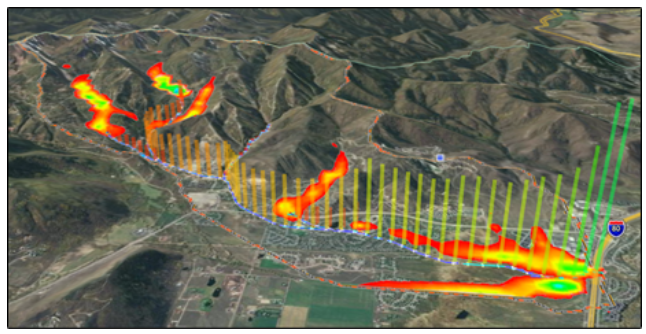
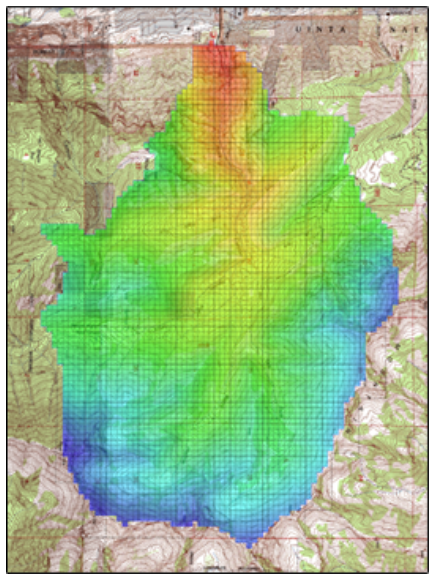
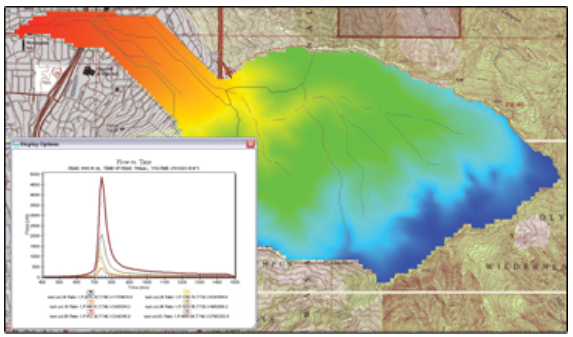
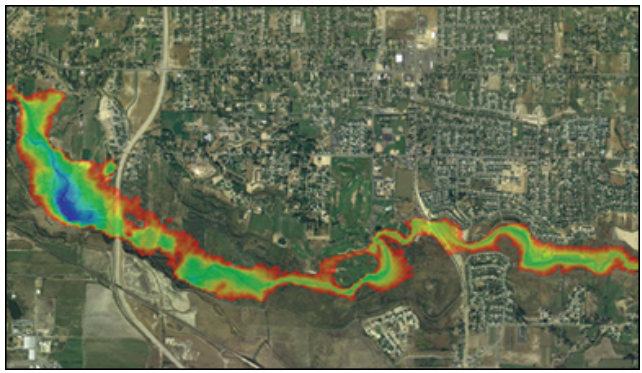
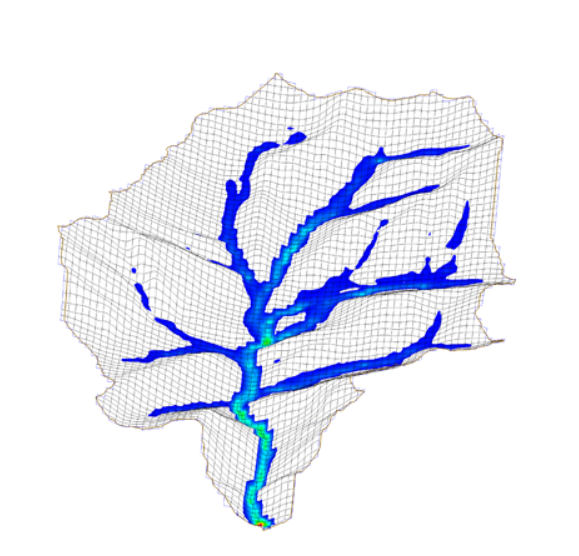
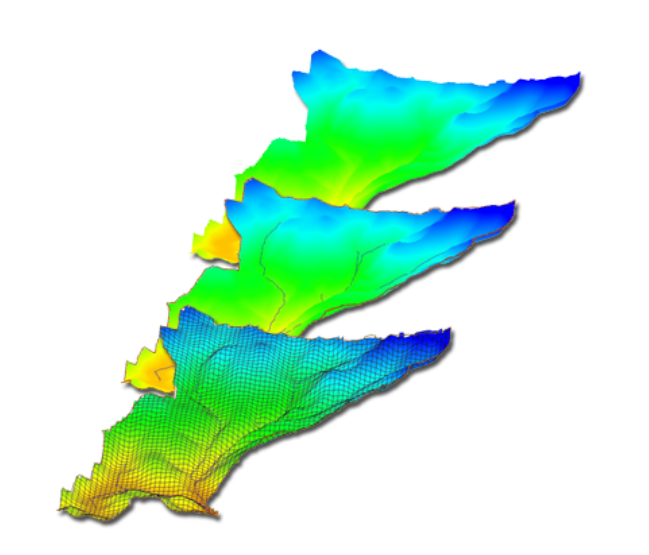
| Models |
Category |
Type |
Method |
|
Description |
| HEC-1 |
Hydrologic Modeling |
1D |
Lumped Parameter |
 |
HEC-1 is a lumped parameter hydrologic model used for modeling single storm events. HEC-1 supports several different options for modeling rainfall, losses, unit hydrographs, and stream routing. |
| HEC-HMS |
Hydrologic Modeling |
1D/2D |
Lumped Parameter/Quasi-Distributed |
 |
HEC-HMS is a lumped parameter/quasi-distributed hydrologic model that includes support for MODClark - a quasi-distributed hydrologic model. HEC-HMS has most of the functionality in HEC-1 and is used for modeling single or multiple storm events. It supports several different options for modeling rainfall, losses, unit hydrographs and stream routing. |
| NSS |
Regression based Hydrologic Modeling |
1D |
Regression-based Single Node |
 |
National Streamflow Statistics (NSS) is based on USGS stream gage station data collected throughout the United States and its territories. NSS is used to determine peak flows at ungaged watersheds based on watershed properties such as area, elevation, mean annual rainfall, and other parameters. |
| TR-20 |
Hydrologic Modeling |
1D |
Lumped Parameter |
 |
TR-20 is a hydrologic model used for computing a runoff hydrograph from a single storm event. It uses standard SCS methods to compute a hydrograph. |
| TR-55 |
Urban Hydrologic Modeling |
1D |
Lumped Parameter |
 |
TR-55 is a subset of the TR-20 hydrologic model. It is used to compute watershed hydrographs for small urban areas from a single storm event. |
| Rational Method |
Urban Hydrologic Modeling |
1D |
Lumped Parameter |
 |
The Rational Method is used for computing peak flows for small urban and rural watersheds. The interface to the Rational Method includes methods for getting a hydrograph and has the capability to combine runoff from multiple basins. The interface includes two different methods for determining peak flows/hydrographs at downstream confluences. |
| MODRAT |
Urban Hydrologic Modeling |
1D |
Lumped Parameter |
 |
Modified Rational Method (MODRAT) uses a variable rainfall intensity to compute flow as well as land use and soil information to compute the runoff coefficient. The model is used for single storm events in small urban areas. |
| OC Rational |
Urban Hydrologic Modeling |
1D |
Lumped Parameter |
 |
OC Rational is used to compute peak flows on small, urban watersheds less than 1 square mile in Orange County, California and includes the ability to combine runoff from multiple basins. |
| OC Hydrograph |
Urban Hydrologic Modeling |
1D |
Lumped Parameter |
 |
OC Hydrograph is used to compute peak flows on watersheds greater than 1 square mile in Orange County, California. |
| HSPF |
Water Quality and Hydrologic Modeling |
1D |
Lumped Parameter |
 |
HSPF is a lumped parameter hydrologic model used for modeling short or long-term watershed quantity and quality for small or large watersheds. The model allows for simulation of hydrology and water quality in natural and man-made systems. |
| EPA SWMM |
Strom Drain Modeling |
1D |
N/A |
 |
EPA-SWMM is a dynamic rainfall-runoff simulation model used for single events or long-term (continuous) simulation of runoff quantity and quality from primarily urban areas. The model includes tools for hydrology, stormwater, sanitary sewer and hydraulic modeling. |
| XP-SWMM |
Strom Drain Modeling |
1D/2D |
N/A |
 |
XP-SWMM is similar to EPA-SWMM with a user-friendly interface which includes the ability to define almost any storm drain or sanitary sewer configuration. The model includes tools for hydrology, stormwater, sanitary sewer and hydraulic modeling. |
| HEC-RAS |
Hydraulic Modeling |
1D |
N/A |
 |
HEC-RAS is a 1D hydraulic model used for steady and unsteady open channel flow computations. HEC-RAS includes tools for running sediment transport and water quality analyses. HEC-RAS is capable of modeling subcritical, supercritical, and mixed flow regime profiles and is able to model inline channel structures such as culverts, weirs, and bridges. |
| SMPDBK |
Dam Break Hydraulic Modeling |
1D |
N/A |
 |
SMPDBK is a hydraulic model used to simulate downstream flooding produced by a dam failure. The model has largely been replaced by the HEC-RAS dam break algorithms, though simulations can still be run using a 32-bit DOS emulator. |
| GSSHA |
Hydrologic, Hydraulic and Groundwater Modeling |
2D |
Finite Difference |
 |
GSSHA is a 2D hydraulic model used for watershed and floodplain analysis of single events or long term studies. GSSHA includes additional capabilities for groundwater modeling, contaminant transport, sediment transport, and storm and tile drain modeling. |
| CE-QUAL-W2 |
Hydrodynamic Reservoir & Estuary Water Quality Modeling |
2D |
Finite Difference |
 |
CE-QUAL is a 2D hydrodynamic model used to evaluate reservoir and estuary water quality. It is primarily used to model fresh water rivers, lakes, and estuaries. |
| HY-8 |
Culvert Analysis |
N/A |
N/A |
 |
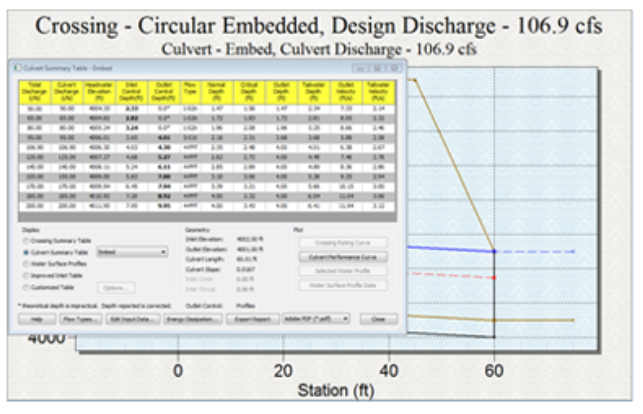
The HY-8 model is used to determine the upstream headwater depth and culvert barrel flow profile for a variety of different culvert configurations. The HY-8 wizard in WMS is used to delineate a watershed upstream from a culvert, compute a hydrograph, and determine the inundated area behind a culvert from an HY-8 analysis. |
| HY-12 |
Strom Drain Modeling |
1D |
HEC-22 |
 |
The HY-12 interface is used to design or analyze a storm drain system. Rational method computations, curbs and gutters, inlets, access holes, pipes, channels, and other storm drain network features can be analyzed using standard FHWA methods with the HY-12 model. |
| Hydraulic Toolbox |
Hydrolic and Hydrologic Modeling |
N/A |
N/A |
 |
The Hydraulic Toolbox includes a number of calculators used to analyze channels, weirs, gutters and inlets, detention basins, and particle gradations. The Hydraulic Toolbox also includes Rational Method hydrologic analysis tools. |
| EPANET |
Water Distribution Modeling |
N/A |
N/A |
 |
EPANET is a widely used water distribution model developed by the US Environmental Protection Agency. WMS now supports reading and editing existing EPANET models as well as reading GIS data files and mapping attributes to the EPANET model attributes. |